How much do we know about the foaming cleaning products we use on a daily basis? Have we ever wondered: what is the role of foam in toiletries?
Why do we tend to choose frothy products?

Through comparison and sorting, we can soon screen out the surface activator with good foaming ability, and also get the foaming law of the surface activator: (ps: Because the same raw material is from different manufacturers, its foam performance is also different, here use different capital letters to represent different raw material manufacturers)
①Among the surfactants, sodium lauryl glutamate has strong foaming ability, and disodium lauryl sulfosuccinate has weak foaming ability.
② Most sulfate surfactants, amphoteric surfactants and non-ionic surfactants have strong foam stabilization ability, while amino acid surfactants generally have weak foam stabilization ability. If you want to develop amino acid surfactant products, you can consider using amphoteric or non-ionic surfactants with strong foaming and foam stabilization ability.
Diagram of foaming force and stable foaming force of the same surfactant:
What is a surfactant?
A surfactant is a compound that contains at least one significant surface affinity group in its molecule (to guarantee its water solubility in most cases) and a non-sexual group for whom there is little affinity. Commonly used surfactants are ionic surfactants (including cationic surfactants and anionic surfactants), non-ionic surfactants, amphoteric surfactants.
Surface activator is the key ingredient for a foaming detergent. How to select the surface activator with good performance is evaluated from the two dimensions of foam performance and degreasing power. Among them, the measurement of foam performance includes two indexes: foaming performance and foam stabilization performance.
Measurement of foam properties
What do we care about bubbles?
It’s just, does it bubble fast? Is there a lot of foam? Will the bubble last?
These questions we will find answers in the determination and screening of raw materials
The main method of our testing is to use the existing equipment, according to the national standard test method – Ross-Miles method (Roche foam determination method) to study, determine and screen the foaming force and foam stability of 31 surfactants commonly used in the laboratory.
Test subjects: 31 surfactants commonly used in laboratories
Test items: foaming force and stable foaming force of different surfactant
Test method: Roth foam tester; Control variable method (equal concentration solution, constant temperature);
Contrast sort
Data processing: record the foam height in different time periods;
The foam height at the beginning of 0min is the foaming force of the table, the higher the height, the stronger the foaming force; The regularity of foam stability was presented in the form of foam height composition charts for 5min, 10min, 30min, 45min and 60min. The longer the foam maintenance time, the stronger the foam stability.
After testing and recording, its data is shown as follows:
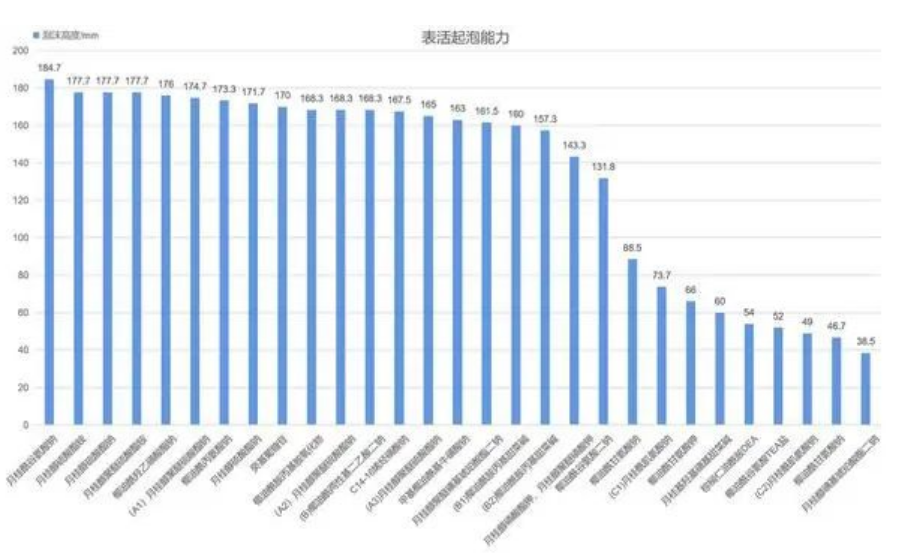
Through comparison and sorting, we can soon screen out the surface activator with good foaming ability, and also get the foaming law of the surface activator: (ps: Because the same raw material is from different manufacturers, its foam performance is also different, here use different capital letters to represent different raw material manufacturers)
① Among the surfactants, sodium lauryl glutamate has strong foaming ability, and disodium lauryl sulfosuccinate has weak foaming ability.
② Most sulfate surfactants, amphoteric surfactants and non-ionic surfactants have strong foam stabilization ability, while amino acid surfactants generally have weak foam stabilization ability. If you want to develop amino acid surfactant products, you can consider using amphoteric or non-ionic surfactants with strong foaming and foam stabilization ability.
Diagram of foaming force and stable foaming force of the same surfactant:
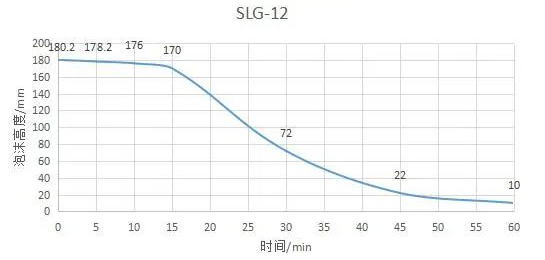
Sodium lauryl glutamate
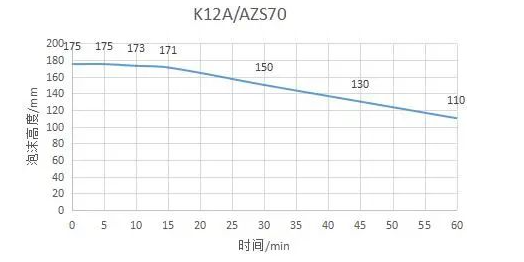
Ammonium lauryl sulfate
There is no correlation between the foaming performance and the foam stabilization performance of the same surfactant, and the foam stabilization performance of the surfactant with good foaming performance may not be good.
Comparison of bubble stability of different surfactant:
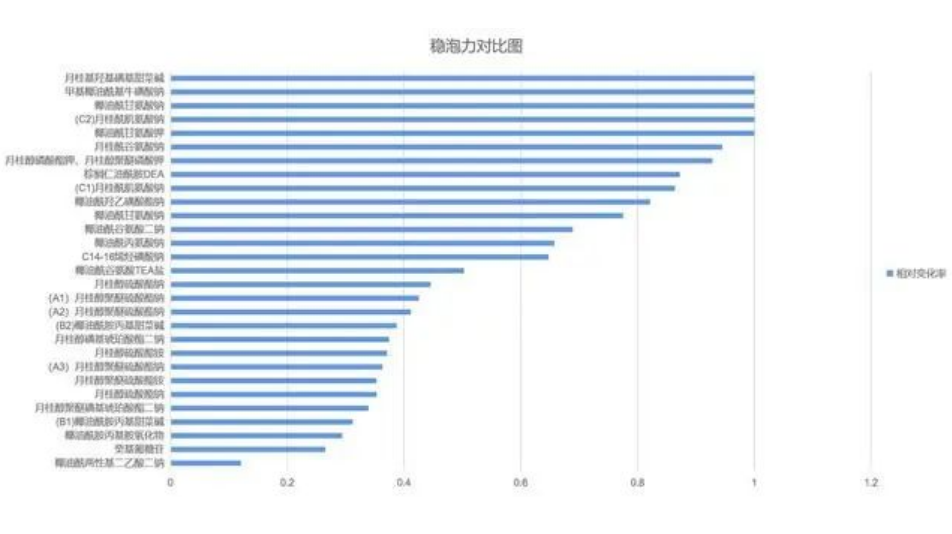
Ps: Relative change rate = (foam height at 0min – foam height at 60min)/foam height at 0min
Evaluation criteria: The greater the relative change rate, the weaker the bubble stabilization ability
Through the analysis of bubble chart, it can be concluded that:
① Disodium cocamphoamphodiacetate has the strongest foam stabilization ability, while lauryl hydroxyl sulfobetaine has the weakest foam stabilization ability.
② The foam stabilization ability of lauryl alcohol sulfate surfactants is generally good, and the foam stabilization ability of amino acid anionic surfactants is generally poor;
Formula design reference:
It can be concluded from the performance of foaming performance and foam stabilization performance of surface activator that there is no certain law and correlation between the two, that is, good foaming performance is not necessarily good foam stabilization performance. This makes us in the screening of surfactant raw materials, we must consider giving full play to the excellent performance of surfactant, the reasonable combination of a variety of surfactant, so as to obtain optimal foam performance. At the same time, it is combined with surfactants with strong degreasing power to achieve the cleaning effect of both foam properties and degreasing power.
Degreasing power test:
Objective: To screen surface activators with strong decongestant ability, and to find out the relationship between foam properties and degreasing power through analysis and comparison.
Evaluation criteria: We compared the data of the stain pixels of the film cloth before and after the surface activator decontamination, calculated the travel value, and formed the degreasing power index. The higher the index, the stronger the degreasing power.
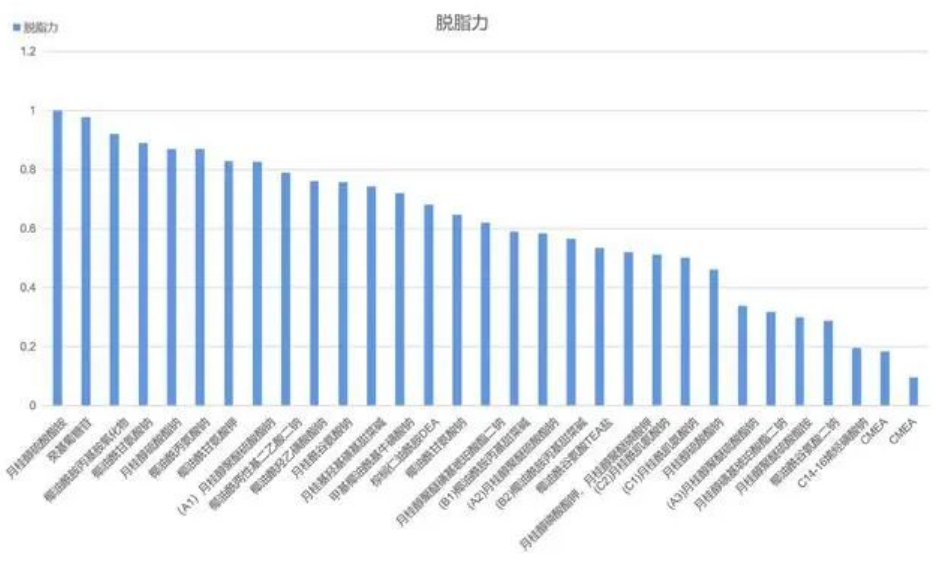
It can be seen from the above data that under the specified conditions, the strong degreasing power is ammonium lauryl sulfate, and the weak degreasing power is two CMEA;
It can be concluded from the above test data that there is no direct correlation between the foam properties of surfactant and its degreasing power. For example, the foam performance of ammonium lauryl sulfate with strong degreasing power is not good. However, the foaming performance of C14-16 olefin sodium sulfonate, which has poor degreasing power, is in the forefront.
So why is it that the more oily your hair, the less frothy it is? (When using the same shampoo).
In fact, this is a universal phenomenon. When you wash your hair with greasier hair, the foam is reduced faster. Does this mean that the foam performance is worse? In other words, is the better the foam performance, the better the degreasing ability?
We already know from the data obtained by the experiment that the foam quantity and foam durability are determined by the foam properties of the surfactant itself, that is, foaming properties and foam stabilization properties. The decontamination ability of surfactant itself will not be weakened by the reduction of foam. This point has also been proved when we have completed the determination of the degreasing ability of the surface activator, the surface activator with good foam properties may not have good degreasing power, and vice versa.
In addition, we can also prove that there is no direct correlation between foam and surfactant degreasing from the different working principles of the two.
Function of surfactant foam:
Foam is a form of surface active agent under specific conditions, its main role is to give the cleaning process a comfortable and pleasant experience, followed by the cleaning of the oil plays an auxiliary role, so that the oil is not easy to settle again under the action of the foam, more easily washed away.
Principle of foaming and degreasing of surfactant:
The surfactant’s cleaning power comes from its ability to reduce oil-water interfacial tension (degreasing), rather than its ability to reduce water-air interfacial tension (foaming).
As we mentioned at the beginning of this article, surfactants are amphiphilic molecules, one of which is hydrophilic and the other is hydrophilic. Therefore, at low concentrations, the surfactant tends to remain on the surface of the water, with the lipophilic (water-hating) end facing outward, first covering the surface of the water, that is, the water-air interface, and thus reducing the tension at this interface.
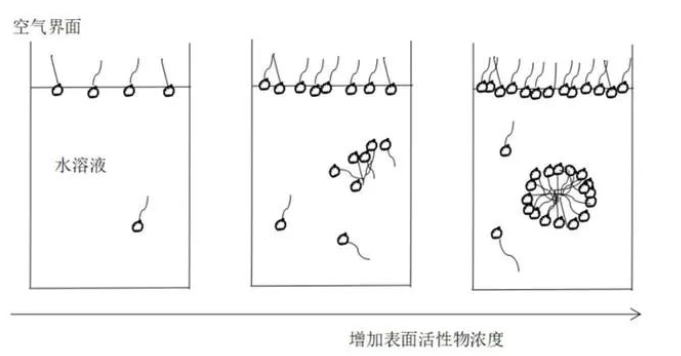
However, when the concentration exceeds a point, the surfactant will start to cluster, forming micelles, and the interfacial tension will no longer drop. This concentration is called the critical micelle concentration.
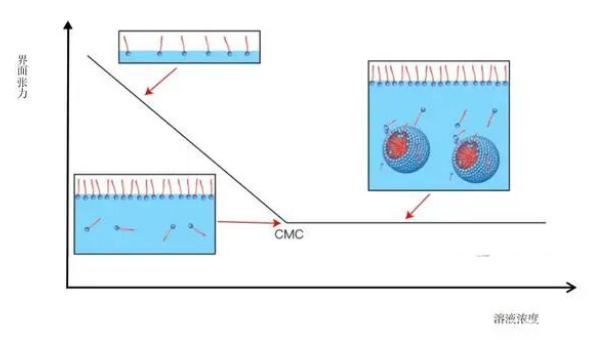
The foaming ability of surfactants is good, indicating that it has a strong ability to reduce the interfacial tension between water and air, and the result of the reduced interfacial tension is that the liquid tends to produce more surfaces (the total surface area of a bunch of bubbles is much larger than that of calm water).
The decontamination power of the surfactant lies in its ability to wet the surface of the stain and emulsify it, that is, to “coat” the oil and allow it to be emulsified and washed off in water.
Therefore, the decontamination ability of the surfactant is linked to its ability to activate the oil-water interface, while the foaming ability only represents its ability to activate the water-air interface, and the two are not completely related. In addition, there are also many non-foaming cleaners, such as the makeup remover and makeup remover oil commonly used in our daily life, which also have a strong decontamination ability, but no foam is produced, and it is obvious that foam and decontamination are not the same thing.
Through the determination and screening of the foam properties of different surfactant, we can clearly get the surfactant with superior foam properties, and then through the determination and sequencing of the degreasing power of surfactant, we have to remove the pollution ability of surfactant. After this collocation, give full play to the advantages of different surfactants, make the surfactants more complete and superior performance, and obtain superior cleaning effect and use experience. In addition, we also realize from the working principle of surfactant that foam is not directly related to cleaning power, and these cognition can help us to have our own judgment and cognition when using a shampoo, so as to choose the product suitable for us.
Post time: Jan-17-2024