-

AES-70 / AE2S / SLES
AES is easily soluble in water, with excellent decontamination, wetting, emulsification, dispersion and foaming properties, good thickening effect, good compatibility, good biodegradation performance (degradation degree up to 99%), mild washing performance will not damage the skin, low irritation to the skin and eyes, is an excellent anionic surfactant.
-

Urea
It is an organic compound composed of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen, one of the simplest organic compounds, and is the main nitrogen-containing end product of protein metabolism and decomposition in mammals and some fish, and urea is synthesized by ammonia and carbon dioxide in industry under certain conditions.
-

Fluorescent Whitening Agent (FWA)
It is a compound with a very high quantum efficiency, in the order of 1 million to 100,000 parts, which can effectively whiten natural or white substrates (such as textiles, paper, plastics, coatings). It can absorb the violet light with a wavelength of 340-380nm and emit blue light with a wavelength of 400-450nm, which can effectively make up for the yellowing caused by the blue light defect of white materials. It can improve the whiteness and brightness of the white material. The fluorescent whitening agent itself is colorless or light yellow (green) color, and is widely used in papermaking, textile, synthetic detergent, plastics, coatings and other industries at home and abroad. There are 15 basic structural types and nearly 400 chemical structures of fluorescent whitening agents that have been industrialized.
-

Sodium Hydrogen Sulfite
In fact, sodium bisulfite is not a true compound, but a mixture of salts that, when dissolved in water, produces a solution composed of sodium ions and sodium bisulfite ions. It comes in the form of white or yellow-white crystals with an odor of sulfur dioxide.
-

Ammonium Bicarbonate
Ammonium bicarbonate is a white compound, granular, plate or columnar crystals, ammonia odor. Ammonium bicarbonate is a kind of carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate has ammonium ion in the chemical formula, is a kind of ammonium salt, and ammonium salt can not be put together with alkali, so ammonium bicarbonate should not be put together with sodium hydroxide or calcium hydroxide.
-

Sodium Bicarbonate
Inorganic compound, white crystalline powder, odorless, salty, soluble in water. It is slowly decomposed in humid air or hot air, producing carbon dioxide, which is completely decomposed when heated to 270 ° C. When exposed to acid, it breaks down strongly, producing carbon dioxide.
-

Sodium Sulfite
Sodium sulfite, white crystalline powder, soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol. Insoluble chlorine and ammonia are mainly used as artificial fiber stabilizer, fabric bleaching agent, photographic developer, dye bleaching deoxidizer, fragrance and dye reducing agent, lignin removal agent for paper making.
-

Calcium Oxide
Quick lime generally contains overheated lime, overheated lime maintenance is slow, if the stone ash paste hardening again, it will cause expansion cracking due to aging expansion. In order to eliminate this harm of lime burning, the lime should also be “aged” for about 2 weeks after maintenance. The shape is white (or gray, brown, white), amorphous, absorbing water and carbon dioxide from the air. Calcium oxide reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and gives off heat. Soluble in acidic water, insoluble in alcohol. Inorganic alkaline corrosive articles, national hazard code :95006. Lime reacts chemically with water and is immediately heated to temperatures above 100°C.
-

Sodium Carbonate
Inorganic compound soda ash, but classified as salt, not alkali. Sodium carbonate is a white powder, tasteless and odorless, easily soluble in water, aqueous solution is strongly alkaline, in humid air will absorb moisture clumps, part of the sodium bicarbonate. The preparation of sodium carbonate includes the joint alkali process, the ammonia alkali process, the Lubran process, etc., and it can also be processed and refined by trona.
-

Potassium Carbonate
An inorganic substance, dissolved as a white crystalline powder, soluble in water, alkaline in aqueous solution, insoluble in ethanol, acetone, and ether. Strong hygroscopic, exposed to the air can absorb carbon dioxide and water, into potassium bicarbonate.
-
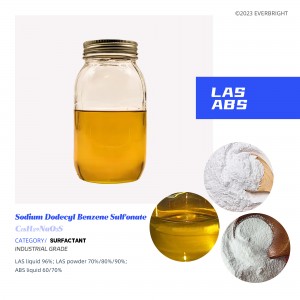
Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate (SDBS/LAS/ABS)
It is a commonly used anionic surfactant, which is a white or light yellow powder/flake solid or brown viscous liquid, difficult to volatilization, easy to dissolve in water, with branched chain structure (ABS) and straight chain structure (LAS), the branched chain structure is small in biodegradability, will cause pollution to the environment, and the straight chain structure is easy to biodegrade, the biodegradability can be greater than 90%, and the degree of environmental pollution is small.
-

Dodecylbenzenesulphonic acid (DBAS/LAS/LABS)
Dodecyl benzene is obtained by condensation of chloroalkyl or α-olefin with benzene. Dodecyl benzene is sulfonated with sulfur trioxide or fuming sulfuric acid. Light yellow to brown viscous liquid, soluble in water, hot when diluted with water. Slightly soluble in benzene, xylene, soluble in methanol, ethanol, propyl alcohol, ether and other organic solvents. It has the functions of emulsification, dispersion and decontamination.